-
1 cable
гибкая нить
Стержень, способный сопротивляться только растяжению.
[Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 82. Строительная механика. Академия наук СССР. Комитет научно-технической терминологии. 1970 г.]Тематики
- строительная механика, сопротивление материалов
EN
DE
FR
электрический кабель
кабель
Кабельное изделие, содержащее одну или более изолированных жил (проводников), заключенных в металлическую или неметаллическую оболочку, поверх которой в зависимости от условий прокладки и эксплуатации может иметься соответствующий защитный покров, в который может входить броня, и пригодное, в частности, для прокладки в земле и под водой.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
кабель
1. Одна или несколько изолированных токопроводящих жил или проводников, заключённых в герметическую оболочку с верхним защитным покрытием
2. Гибкий несущий элемент висячих систем, кабель-кранов и канатных подвесных дорог
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель электрический
Кабель 1. для передачи на расстояние электрической энергии либо сигналов высокого или низкого напряжений
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель
Один или несколько скрученных изолированных гибких проводников, предназначенных для обматывания объектов контроля в целях их продольного или тороидного намагничивания.
кабель
Экранированный проводник, соединяющий электронный блок с преобразователем или электронные блоки между собой
кабель
-
[IEV number 151-12-38]EN
cable
assembly of one or more conductors and/or optical fibres, with a protective covering and possibly filling, insulating and protective material
[IEV number 151-12-38]FR
câble, m
assemblage d'un ou plusieurs conducteurs ou fibres optiques, muni d'une enveloppe protectrice et éventuellement de matériaux de remplissage, d'isolation et de protection
[IEV number 151-12-38]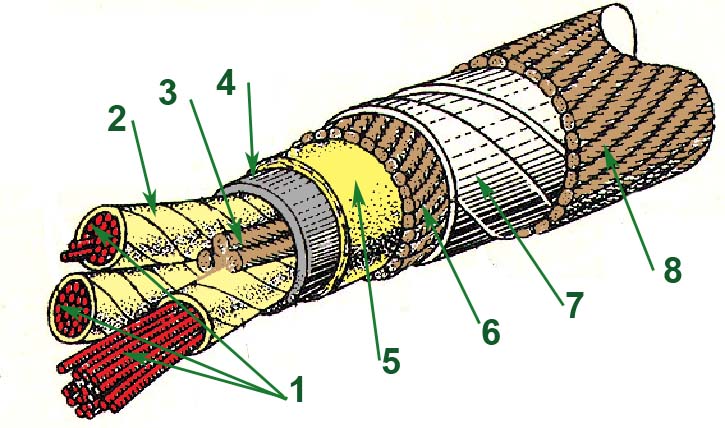
Пример конструкции кабеля:
1 - Токопроводящие жилы;
2 - Бумага, пропитанная маслом;
3 - Джутовый заполнитель;
4 - Свинцовая оболочка;
5 - Бумажная лента;
6 - Прослойка из джута;
7 - Стальная ленточная броня;
8 - Джутовый покров.
Кабели на напряжение до 1 кВ и выше...
[ГОСТ 12.2.007.14-75]
... силовые кабели с медными или алюминиевыми жилами с резиновой изоляцией, в свинцовой, поливинилхлоридной или резиновой оболочке, с защитными покровами или без них, предназначенные для неподвижной прокладки в электрических сетях напряжением 660 В переменного тока частотой 50 Гц или 1000 В постоянного тока и на напряжение 3000, 6000 и 10000 В постоянного тока.
Кабели предназначены для прокладки:
- на трассах с неограниченной разностью уровней.
- внутри помещений, в каналах, туннелях, в местах, не подверженных вибрации, в условиях отсутствия механических воздействий на кабель..
- в земле (траншеях), если кабель не подвергается значительным растягивающим усилиям
Строительная длина кабелей должна быть не менее 125 м. Допускаются маломерные отрезки длиной не менее 20 м в количестве не более 10 % от общей длины сдаваемой партии кабелей.
[ ГОСТ 433-73]
... монтажные многожильные кабели с поливинилхлоридной изоляцией и оболочкой, предназначенные для фиксированного межприборного монтажа электрических устройств, работающих при номинальном переменном напряжении до 500 В частоты до 400 Гц или постоянном напряжении до 750 В.
Требования к стойкости при механических воздействиях
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии вибрационных нагрузок в диапазоне частот 1-5000 Гц с ускорением до 392 м/с2 (40 g).
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии многократных ударов с ускорением 1471 м/с2 (150 g) при длительности удара 1-3 мс.
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии одиночных ударов с ускорением 9810 м/с2(1000 g) и линейных нагрузок с ускорением до 4905 м/с2 (500 g).
Требования к стойкости при климатических воздействиях
-Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию повышенной температуры 343 К (70°С), при этом за повышенную температуру принимают температуру наиболее нагреваемого элемента конструкции кабеля.
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию пониженной температуры - 223 К (минус 50°С).
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию относительной влажности воздуха до 98 % при температуре 308 К (35°С).
- Кабели климатического исполнения Т должны быть стойкими к воздействию плесневых грибов.
[ ГОСТ 10348-80]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- вводить кабель в отверстие
- вводить кабель в эксплуатацию
- наматывать кабель на барабан
- подключать кабель
- присоединять кабель
- прокладывать кабель
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- неподвижная прокладка
- прокладка кабеля
- прокладка кабеля в земляной траншее
- прокладка кабеля непосредственно в грунте
- фиксированный межприборный монтаж электрических устройств
EN
DE
FR
электрический провод
провод
Кабельное изделие, содержащее одну или несколько скрученных проволок или одну или более изолированных жил, поверх оторых в зависимости от условий прокладки и эксплуатации может иметься легкая неметаллическая оболочка, обмотка и (или) оплетка из волокнистых материалов или проволоки, и не предназначенное, как правило, для прокладки в земле.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
провод электрический
Металлический проводник, состоящий из одной или нескольких проволок, служащий для передачи и распределения электрической энергии
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > cable
-
2 câble électrique
электрический кабель
кабель
Кабельное изделие, содержащее одну или более изолированных жил (проводников), заключенных в металлическую или неметаллическую оболочку, поверх которой в зависимости от условий прокладки и эксплуатации может иметься соответствующий защитный покров, в который может входить броня, и пригодное, в частности, для прокладки в земле и под водой.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
кабель
1. Одна или несколько изолированных токопроводящих жил или проводников, заключённых в герметическую оболочку с верхним защитным покрытием
2. Гибкий несущий элемент висячих систем, кабель-кранов и канатных подвесных дорог
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель электрический
Кабель 1. для передачи на расстояние электрической энергии либо сигналов высокого или низкого напряжений
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель
Один или несколько скрученных изолированных гибких проводников, предназначенных для обматывания объектов контроля в целях их продольного или тороидного намагничивания.
кабель
Экранированный проводник, соединяющий электронный блок с преобразователем или электронные блоки между собой
кабель
-
[IEV number 151-12-38]EN
cable
assembly of one or more conductors and/or optical fibres, with a protective covering and possibly filling, insulating and protective material
[IEV number 151-12-38]FR
câble, m
assemblage d'un ou plusieurs conducteurs ou fibres optiques, muni d'une enveloppe protectrice et éventuellement de matériaux de remplissage, d'isolation et de protection
[IEV number 151-12-38]
Пример конструкции кабеля:
1 - Токопроводящие жилы;
2 - Бумага, пропитанная маслом;
3 - Джутовый заполнитель;
4 - Свинцовая оболочка;
5 - Бумажная лента;
6 - Прослойка из джута;
7 - Стальная ленточная броня;
8 - Джутовый покров.
Кабели на напряжение до 1 кВ и выше...
[ГОСТ 12.2.007.14-75]
... силовые кабели с медными или алюминиевыми жилами с резиновой изоляцией, в свинцовой, поливинилхлоридной или резиновой оболочке, с защитными покровами или без них, предназначенные для неподвижной прокладки в электрических сетях напряжением 660 В переменного тока частотой 50 Гц или 1000 В постоянного тока и на напряжение 3000, 6000 и 10000 В постоянного тока.
Кабели предназначены для прокладки:
- на трассах с неограниченной разностью уровней.
- внутри помещений, в каналах, туннелях, в местах, не подверженных вибрации, в условиях отсутствия механических воздействий на кабель..
- в земле (траншеях), если кабель не подвергается значительным растягивающим усилиям
Строительная длина кабелей должна быть не менее 125 м. Допускаются маломерные отрезки длиной не менее 20 м в количестве не более 10 % от общей длины сдаваемой партии кабелей.
[ ГОСТ 433-73]
... монтажные многожильные кабели с поливинилхлоридной изоляцией и оболочкой, предназначенные для фиксированного межприборного монтажа электрических устройств, работающих при номинальном переменном напряжении до 500 В частоты до 400 Гц или постоянном напряжении до 750 В.
Требования к стойкости при механических воздействиях
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии вибрационных нагрузок в диапазоне частот 1-5000 Гц с ускорением до 392 м/с2 (40 g).
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии многократных ударов с ускорением 1471 м/с2 (150 g) при длительности удара 1-3 мс.
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии одиночных ударов с ускорением 9810 м/с2(1000 g) и линейных нагрузок с ускорением до 4905 м/с2 (500 g).
Требования к стойкости при климатических воздействиях
-Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию повышенной температуры 343 К (70°С), при этом за повышенную температуру принимают температуру наиболее нагреваемого элемента конструкции кабеля.
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию пониженной температуры - 223 К (минус 50°С).
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию относительной влажности воздуха до 98 % при температуре 308 К (35°С).
- Кабели климатического исполнения Т должны быть стойкими к воздействию плесневых грибов.
[ ГОСТ 10348-80]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- вводить кабель в отверстие
- вводить кабель в эксплуатацию
- наматывать кабель на барабан
- подключать кабель
- присоединять кабель
- прокладывать кабель
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- неподвижная прокладка
- прокладка кабеля
- прокладка кабеля в земляной траншее
- прокладка кабеля непосредственно в грунте
- фиксированный межприборный монтаж электрических устройств
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > câble électrique
-
3 blindage (d'un câble)
общий экран (кабеля)
Наложенный на кабель заземленный металлический слой, ограничивающий электрическое поле в пределах кабеля и (или) защищающий кабель от внешнего электрического воздействия
Примечание. Металлические оболочки, фольга, оплетки, броня и заземленные концентрические токопроводящие жилы могут также служить в качестве общих экранов
[IEV number 461-03-04]EN
shield (of a cable)
surrounding earthed metallic layer which serves to confine the electric field within the cable and/or to protect the cable from external electrical influence
NOTE 1 – Metallic sheaths, foils, braids, armours and earthed concentric conductors may also serve as shields.
NOTE 2 – In French, the term "blindage" may be used when the main purpose of the screen is the protection from exterlnal electrical influence.
[IEV number 461-03-04]FR
écran métallique (d'un câble)
blindage (d'un câble)
couche métallique disposée autour des conducteurs et mise à la terre afin de maintenir le champ électrique du câble à l'intérieur de celui-ci et/ou de protéger le câble des influences électriques externes
NOTE 1 – Les gaines métalliques, les rubans métalliques, les tresses métalliques, les armures, et les âmes concentriques mises à la terre peuvent également servir d'écrans de protection.
NOTE 2 – En français, le terme « blindage » peut être utilisé lorsque l'écran a pour objet principal la protection contre les influences électriques externes.
[IEV number 461-03-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > blindage (d'un câble)
-
4 écran métallique (d'un câble)
общий экран (кабеля)
Наложенный на кабель заземленный металлический слой, ограничивающий электрическое поле в пределах кабеля и (или) защищающий кабель от внешнего электрического воздействия
Примечание. Металлические оболочки, фольга, оплетки, броня и заземленные концентрические токопроводящие жилы могут также служить в качестве общих экранов
[IEV number 461-03-04]EN
shield (of a cable)
surrounding earthed metallic layer which serves to confine the electric field within the cable and/or to protect the cable from external electrical influence
NOTE 1 – Metallic sheaths, foils, braids, armours and earthed concentric conductors may also serve as shields.
NOTE 2 – In French, the term "blindage" may be used when the main purpose of the screen is the protection from exterlnal electrical influence.
[IEV number 461-03-04]FR
écran métallique (d'un câble)
blindage (d'un câble)
couche métallique disposée autour des conducteurs et mise à la terre afin de maintenir le champ électrique du câble à l'intérieur de celui-ci et/ou de protéger le câble des influences électriques externes
NOTE 1 – Les gaines métalliques, les rubans métalliques, les tresses métalliques, les armures, et les âmes concentriques mises à la terre peuvent également servir d'écrans de protection.
NOTE 2 – En français, le terme « blindage » peut être utilisé lorsque l'écran a pour objet principal la protection contre les influences électriques externes.
[IEV number 461-03-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > écran métallique (d'un câble)
-
5 rouleau
1. masculine nouna. ( = bande, cylindre) roll• rouleau de papier/tissu/pellicule roll of paper/material/filmb. ( = outil, ustensile) rollerc. ( = vague) rollerd. ( = saut) roll2. compounds* * *pl rouleaux ʀulo nom masculin1) ( cylindre) roll2) ( grosse vague) breaker, roller3) Agriculture, Technologie roller4) ( bigoudi) roller, curler5) Sportsauter en rouleau — ( en ventral) to straddle; ( en dorsal) to flop
6) ( pour peindre) roller•Phrasal Verbs:••être au bout du rouleau — (colloq) ( nerveusement) to be at the end of one's tether; ( être mourant) to be at death's door
* * *ʀulorouleaux pl nm1) [papier, tissu, pièces de monnaie] rollêtre au bout du rouleau fig (= être exténué) — to be at the end of one's tether, (= être à la fin de sa vie) [personne] to be at death's door
2) (= vague) roller3) SPORT roll4) [machine à écrire] roller5) (à mise en plis, à peinture) roller* * *1 ( cylindre) roll; rouleau de papier hygiénique/d'essuie-tout/de papier peint roll of toilet paper/of paper towels/of wallpaper; ce papier peint fait 15 euros le rouleau this wallpaper is 15 euros a roll; j'ai besoin de trois rouleaux pour refaire la cuisine I need three rolls to do ou paper the kitchen; un rouleau de parchemin/fil électrique/papier aluminium a roll of parchment/electrical cable/tin foil; un rouleau de pièces de monnaie a roll of coins; se vendre au rouleau to be sold by the roll; acheter de la moquette en rouleau to buy a roll of carpet; le revêtement existe en dalles ou en rouleau you can get this covering in tiles or in a roll;2 ( grosse vague) breaker, roller;4 ( bigoudi) roller, curler;5 Sport rouleau ventral straddle (roll); rouleau dorsal flop; sauter en rouleau ( en ventral) to straddle; ( en dorsal) to flop;6 ( pour peindre) roller.rouleau compresseur Tech roadroller, steamroller; fig steamroller; rouleau à pâtisserie Culin rolling pin; étendre la pâte au rouleau roll out the pastry with a rolling pin; rouleau de peintre Tech paintroller; peindre le plafond au rouleau to paint the ceiling with a roller; rouleau de printemps Culin spring roll.être au bout du rouleau○ ( nerveusement) to be at the end of one's tether; ( être mourant) to be at death's door.( pluriel masculin rouleaux) [rulo] nom masculin1. [de papier, de tissu etc.] rollrouleau de parchemin roll ou scroll of parchment2. [outil - de peintre, de jardinier, de relieur] rollerrouleau imprimeur ou encreur (press) cylinder4. CUISINE5. SPORT6. [vague] rollera. (sens propre) [à gazole] roadrollerb. [à vapeur] steamroller -
6 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
7 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
8 tension assignée
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > tension assignée
-
9 tension nominale
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
номинальное напряжение конденсатора
Максимальное напряжение, при котором конденсатор может работать в течение минимальной наработки в условиях, указанных в нормативно-технической документации
[ ГОСТ 21415-75]
номинальное напряжение конденсатора
Действующее значение синусоидального переменного напряжения при номинальной частоте, на которое рассчитан конденсатор. Номинальное напряжение многофазного конденсатора - значение напряжения между выводами.
[ ГОСТ 1282-88]Тематики
- конденсаторы для повыш. коэф. мощности
- конденсаторы для электронной аппаратуры
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > tension nominale
-
10 Un
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Un
-
11 canalisation préfabriquée
система сборных шин
шинопровод
Устройство, представляющее собой систему проводников, состоящее из шин, установленных на опорах из изоляционного материала или в каналах, коробах или подобных оболочках, и прошедшее типовые испытания.
Устройство может состоять из следующих элементов:
- прямые секции с узлами ответвления или без них;
- секции для изменения положения фаз, разветвления, поворота, а также вводные и переходные;
- секции ответвленные.
Примечание — Термин «шинопровод» не определяет геометрическую форму, габариты и размеры проводников.
(МЭС 441-12-07, с изменением)
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ПУЭ]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1000 В заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ОСТ 36-115-85]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1 кВ, предназначенный для передачи и распределения электроэнергии, состоящий из неизолированных или изолированных проводников (шин) и относящихся к ним изоляторов, защитных оболочек, ответвительных устройств, поддерживающих и опорных конструкций.
[ ГОСТ Р 53310-2012]EN
busway
A prefabricated assembly of standard lengths of busbars rigidly supported by solid insulation and enclosed in a sheet-metal housing.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/busway]
busway
Busway is defined by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) as a prefabricated electrical distribution system consisting of bus bars in a protective enclosure, including straight lengths, fittings, devices, and accessories. Busway includes bus bars, an insulating and/or support material, and a housing.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]1.1. Шинопроводы по назначению подразделяются на:
- распределительные, предназначенные для распределения электрической энергии;
- магистральные, предназначенные для передачи электрической энергии от источника к месту распределения (распределительным пунктам, распределительным шинопроводам) или мощным приемникам электрической энергии.
1.2. По конструктивному исполнению шинопроводы подразделяются на:
- трехфазные;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим проводником;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим и нулевым защитным проводником.
2. Основные параметры и размеры
2.1. Основные элементы шинопроводов
2.1.1. Основными элементами распределительных шинопроводов являются:а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линии, имеющие места для присоединения одного или двух ответвительных устройств для секций длиной до 2 м включительно, двух, трех, четырех или более - для секций длиной 3 м;
б) прямые прогоночные секции - для прямолинейных участков линий, где присоединение ответвительных устройств не требуется;
в) угловые секции - для поворотов линии на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) вводные секции или вводные коробки с коммутационной, защитной и коммутационной аппаратурой или без нее - для подвода питания к шинопроводам кабелем, проводами или шинопроводом;
д) переходные секции или устройства - для соединения двух шинопроводов на различные номинальные токи или шинопроводов разных конструкций;
е) ответвительные устройства (коробки, штепсели) - для разъемного присоединения приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и с предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем;
з) присоединительные фланцы - для сочленения оболочек шинопроводов с оболочками щитов или шкафов;
и) торцовые крышки (заглушки) - для закрытия торцов крайних секций шинопровода;
к) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;2.1.2. Основными элементами магистральных шинопроводов являются:
а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линий;
б) угловые секции - для поворотов линий на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
в) тройниковые секции - для разветвления в трех направлениях под углом 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) подгоночные секции - для подгонки линии шинопроводов до необходимой длины;
д) разделительные секции с разъединителем - для секционирования магистральных линий шинопроводов;
е) компенсационные секции - для компенсации температурных изменений длины линии шинопроводов;
ж) переходные секции - для соединения шинопроводов на разные номинальные токи;
з) ответвительные устройства (секции, коробки) - для неразборного, разборного или разъемного присоединения распределительных пунктов, распределительных шинопроводов или приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем; секции могут выпускаться без указанных аппаратов;
и) присоединительные секции - для присоединения шинопроводов к комплектным трансформаторным подстанциям;
к) проходные секции - для прохода через стены и перекрытия;
л) набор деталей и материалов для изолирования мест соединения секций шинопроводов с изолированными шинами;
м) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;
н) крышки (заглушки) торцовые и угловые для закрытия торцов концевых секций шинопровода и углов.
2.2.3. В зависимости от вида проводников токопроводы подразделяются на гибкие (при использовании проводов) и жесткие (при использовании жестких шин).
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями, называется шинопроводом.
В зависимости от назначения шинопроводы подразделяются на:- магистральные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним распределительных шинопроводов и силовых распределительных пунктов, щитов и отдельных мощных электроприемников;
- распределительные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним электроприемников;
- троллейные, предназначенные для питания передвижных электроприемников;
- осветительные, предназначенные для питания светильников и электроприемников небольшой мощности.
[ПУЭ, часть 2]
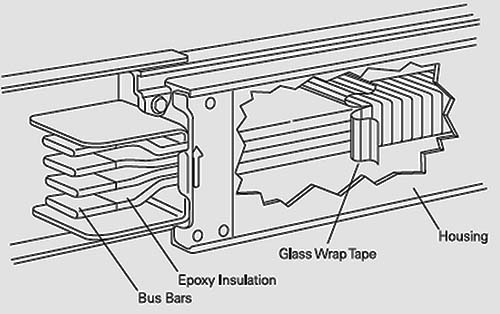
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/standards-and-applications-of-medium-voltage-bus-duct]
Конструкция шинопровода на среднее напряжениеПараллельные тексты EN-RU
A major advantage of busway is the ease in which busway sections are connected together.
Electrical power can be supplied to any area of a building by connecting standard lengths of busway.
It typically takes fewer man-hours to install or change a busway system than cable and conduit assemblies.Основное преимущество шинопровода заключается в легкости соединения его секций.
Соединяя эти стандартные секции можно легко снабдить электроэнергией любую часть здания.
Как правило, установить или изменить систему шинопроводов занимает гораздо меньше времени, чем выполнить аналогичные работы, применяя разводку кабелем в защитных трубах.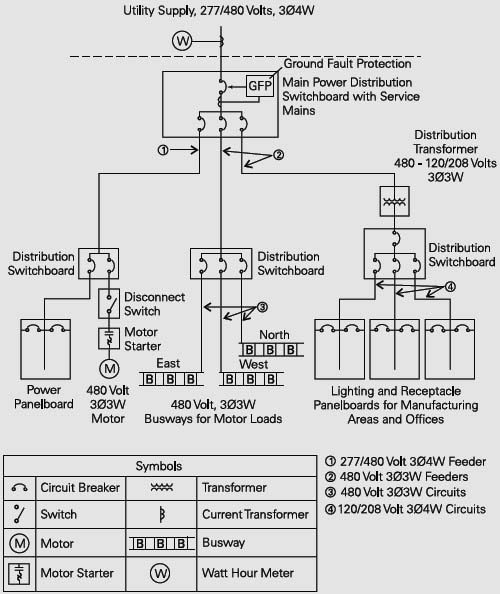
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
The total distribution system frequently consists of a combination of busway and cable and conduit.
In this example power from the utility company is metered and enters the plant through a distribution switchboard.
The switchboard serves as the main disconnecting means.Как правило, распределение электроэнергии производится как через шинопроводы, так и через проложенные в защитных трубах кабели.
В данном примере поступающая от питающей сети электроэнергия измеряется на вводе в главное распределительный щит (ГРЩ).
ГРЩ является главным коммутационным устройством.
The feeder on the left feeds a distribution switchboard, which in turn feeds a panelboard and a 480 volt, three-phase, three-wire (3Ø3W) motor.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная слева, питает распределительный щит, который в свою очередь питает групповой щиток и электродвигатель.
Электродвигатель получает питание через трехфазную трехпроводную линию напряжением 480 В.The middle feeder feeds another switchboard, which divides the power into three, three-phase, three-wire circuits. Each circuit feeds a busway run to 480 volt motors.
Средняя (на чертеже) распределительная цепь питает другой распределительный щит, от которого электроэнергия распределяется через три трехфазные трехпроводные линии на шинопроводы.
Каждый шинопровод используется для питания электродвигателей напряжением 480 В.The feeder on the right supplies 120/208 volt power, through a step-down transformer, to lighting and receptacle panelboards.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная справа, питает напряжением 120/208 В через понижающий трансформатор щитки для отдельных групп светильников и штепсельных розеток.
Branch circuits from the lighting and receptacle panelboards supply power for lighting and outlets throughout the plant.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]Групповые электрические цепи, идущие от групповых щитков, предназначены для питания всех светильников и штепсельных розеток предприятия.
[Перевод Интент]Selection of the busbar trunking system based on voltage drop.
[Legrand]Выбор шинопровода по падению напряжения.
[Перевод Интент]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Обобщающие термины
Близкие понятия
- электропроводки, выполненные шинопроводами
Действия
- выбор шинопровода по...
- крепление шинопровода к опорным конструкциям
- монтаж шинопроводов
- применение шинопроводов в пожароопасных зонах
- проектирование шинопровода
- прокладка шинопровода
Сопутствующие термины
- вертикальный участок шинопровода
- горизонтальный участок шинопровода
- прямой участок шинопровода
- устройства для крепления шинопроводов
- шинопровод переменного тока на 1600 А
- электрическая сеть, выполняемая шинопроводами
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > canalisation préfabriquée
-
12 ensemble d'appareillage pour réseau de distribution
распределительный шкаф
Комплектное устройство шкафного типа для стационарной наружной установки, предназначенное для распределения электрической энергии посредством кабеля для другого оборудования. Это другое оборудование не предназначено для потребления электрической энергии (см. рисунок 1).
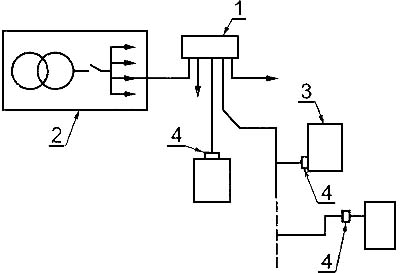
Рисунок 1 - Типовая распределительная сеть
1 - распределительный шкаф;
2 - подстанция (высокое напряжение/низкое напряжение);
3 - потребители;
4 - точки соединений
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 5-99 ( МЭК 60439-5-98)]EN
cable distribution cabinet
CDC
cubicle-type assembly for outdoor installation which in use receives electrical energy via cables from one or more substation cable distribution boards (SCDBs), and distributes that energy through one or more cables to other equipment
NOTE This other equipment is not intended to consume electrical energy.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]FR
ensemble d'appareillage pour réseau de distribution
ERD
ensemble en armoire pour installation extérieure qui, lors de son utilisation, reçoit de l’énergie électrique via des câbles d’un ou plusieurs tableaux de distribution par câbles pour poste (SCDB) et, distribue cette énergie par un ou plusieurs câbles à d’autres matériels
NOTE Ces autres matériels ne sont pas conçus pour consommer de l'énergie électrique.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ensemble d'appareillage pour réseau de distribution
-
13 ERD
распределительный шкаф
Комплектное устройство шкафного типа для стационарной наружной установки, предназначенное для распределения электрической энергии посредством кабеля для другого оборудования. Это другое оборудование не предназначено для потребления электрической энергии (см. рисунок 1).

Рисунок 1 - Типовая распределительная сеть
1 - распределительный шкаф;
2 - подстанция (высокое напряжение/низкое напряжение);
3 - потребители;
4 - точки соединений
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 5-99 ( МЭК 60439-5-98)]EN
cable distribution cabinet
CDC
cubicle-type assembly for outdoor installation which in use receives electrical energy via cables from one or more substation cable distribution boards (SCDBs), and distributes that energy through one or more cables to other equipment
NOTE This other equipment is not intended to consume electrical energy.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]FR
ensemble d'appareillage pour réseau de distribution
ERD
ensemble en armoire pour installation extérieure qui, lors de son utilisation, reçoit de l’énergie électrique via des câbles d’un ou plusieurs tableaux de distribution par câbles pour poste (SCDB) et, distribue cette énergie par un ou plusieurs câbles à d’autres matériels
NOTE Ces autres matériels ne sont pas conçus pour consommer de l'énergie électrique.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ERD
-
14 canalisation
выправление рек
Комплекс мероприятий по упорядочению русла рек с целью создания благоприятных условий судоходства и лесосплава, уменьшения размывов русла рек и подмыва берегов.
[ ГОСТ 19185-73]
Тематики
EN
DE
FR
канал
Закрытый желоб, предназначенный специально для размещения и защиты электрических проводов, кабелей и электрических шин.
Трубопроводы, кабельнесущие системы и короба под полом являются модификациями каналов.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
канал
канал для электропроводки
Обобщающий термин для обозначния закрытых полых конструкций, предназначенных для прокладки в них и для механической защиты кабелей и проводов.
Примечание
К каналам для прокладки кабелей и проводов относятся: трубы для электропроводки, системы кабельных коробов, в том числе и размещаемые в полу
Примечание автора карточки
Шинопроводы (busbars), указанные в IEC 60204-1-2006, не относятся к констукциям для прокладки в них кабелей и проводов.
[Интент]EN
duct
enclosed channel designed expressly for holding and protecting electrical conductors, cables, and busbars
NOTE
Conduits (see 3.7), cable trunking systems (see 3.5) and underfloor channels are types of duct.
[IEC 60204-1, ed. 5.0 (2005-10)]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
canalisation
canal fermé destiné expressément au support et à la protection de conducteurs, de câbles et de barres électriques
NOTE Les conduits (voir 3.7), les systèmes de goulottes (voir 3.5) et les canaux enterrés sont des types de canalisations.
[IEC 60204-1, ed. 5.0 (2005-10)]Термин "канал" применяют также при описании сооружений местных линейных телефонных сетей, см:
- канал трубопровода кабельной канализации;
- трубный канал
2.1.4..... При скрытой электропроводке применяются следующие способы прокладки проводов и кабелей: в трубах, гибких металлических рукавах, коробах, замкнутых каналах и пустотах строительных конструкций, в заштукатуриваемых бороздах, под штукатуркой, а также замоноличиванием в строительные конструкции при их изготовлении.
2.1.15. В стальных и других механических прочных трубах, рукавах, коробах, лотках и замкнутых каналах строительных конструкций зданий допускается совместная прокладка проводов и кабелей (за исключением взаиморезервируемых).
2.1.19. При прокладке проводов и кабелей в трубах, глухих коробах, гибких металлических рукавах и замкнутых каналах должна быть обеспечена возможность замены проводов и кабелей.
2.1.20. Конструктивные элементы зданий и сооружений, замкнутые каналы и пустоты которых используются для прокладки проводов и кабелей, должны быть несгораемыми.
[ПУЭ]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
External ducts
Conductors and their connections external to the electrical equipment enclosure(s) shall be enclosed in suitable ducts (i.e. conduit or cable trunking systems) as described in 13.5 except for suitably protected cables that may be installed without ducts and with or without the use of open cable trays or cable support means.
[IEC 60204-1-2006]Каналы для электропроводок, прокладываемые вне оболочек
Проводники вне оболочек электротехнических устройств, должны прокладываться, а их соединения должны выполняться в соответствующих каналах для электропроводок (т. е. в трубах или в системах кабельных коробов) в соответствии с п. 13.5 за исключением надлежащим образом защищенных кабелей, которые можно прокладывать вне каналов с или без использования открытых (т. е. без крышек) кабельных лотков или опорных кабельных конструкций.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
FR
канализация
Комплекс инженерных сооружений и оборудования, обеспечивающих сбор и отведение за пределы населённых мест и промышленных предприятий сточных вод, а также их очистку и обеззараживание перед утилизацией или сбросом в водоём
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
канализация
Отведение бытовых, промышленных и ливневых сточных вод
[ ГОСТ 19185-73]
[ ГОСТ 25150-82]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
системы распределения
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
channelling
Any system of distribution canals or conduits for water, gas, electricity, or steam. (Source: MGH)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > canalisation
-
15 fiche
- наконечник (в медицинском оборудовании)
- карта технологическая
- кабельная вилочная (розеточная) часть электрического соединителя
- вилка кабельная
- вилка
вилка
Часть соединителя, имеющая штыри для осуществления контакта с розеткой и средства для электрического соединения и закрепления гибкого кабеля
[ ГОСТ Р 51322.1-99]
вилка
Часть соединителя, которая выполняется как одно целое или непосредственно прикрепляется к гибкому кабелю, подсоединяемому к аппарату или переносной розетке.
[ ГОСТ Р 51323.1-99]
вилка (кабельная вилка)
Часть соединителя, которая выполняется как одно целое и прикрепляется к гибкому кабелю, подсоединяемому к электроприбору или переносной розетке.
Примечание — Вилка кабельного соединителя аналогична вилке штепсельного соединителя
[ ГОСТ Р 51323.1-99]
вилка
-
[IEV number 442-03-01]EN
plug
the part integral with or intended to be attached directly to one flexible cable connected to the equipment or to a connector
[IEC 60309-1, ed. 4.0 (1999-02)]
plug
the part integral with or intended to be attached to one flexible cable connected to the equipment or to a connector
NOTE The plug of a cable coupler is identical to the plug of a "plug and socket-outlet".
[IEC 60309-1, ed. 4.0 (1999-02)]
plug
accessory having pins designed to engage with the contacts of a socket-outlet, also incorporating means for the electrical connection and mechanical retention of flexible cables or cords
[IEV number 442-03-01]FR
fiche
partie faisant corps avec le câble souple raccordé au matériel ou à une prise mobile ou destinée à être reliée directement à un tel câble
[IEC 60309-1, ed. 4.0 (1999-02)]
fiche
partie faisant corps avec le câble souple raccordé au matériel ou à une prise mobile ou destinée à être reliée à un tel câble
NOTE La fiche d'un prolongateur est identique à la fiche d'une prise de courant.
[IEC 60309-1, ed. 4.0 (1999-02)]
fiche
appareil pourvu de broches conçues pour s'engager dans les contacts d'un socle de prise de courant et comprenant également des pièces pour la connexion électrique et la retenue mécanique des câbles souples
[IEV number 442-03-01]

Вилка (опрессованная) бытового назначения
(Кабельная) вилка (разборная) промышленного назначения
Рис. ABB
1 - Розетка стационарная
2 - Вилка опрессованная
3 - Удлиннитель одноместный
4 - Соединитель штепсельный
5 - Розетка переносная опрессованная
6 - Вилка опрессованная
7 - Соединитель штепсельный
8 - Розетка приборная
9 - Удлинитель с приборной розеткой
10 - Вилка приборная
11 - Прибор
12 - Соединитель приборный
[ ГОСТ Р 51322.1-99]Форма и длина вилки должны обеспечивать ее свободное отключение рукой от соответствующей розетки.
[ ГОСТ 28244-96]
6.6.25. Вилки штепсельных соединителей должны быть выполнены таким образом, чтобы их нельзя было включать в розетки сети с более высоким номинальным напряжением, чем номинальное напряжение вилки. Конструкция розеток и вилок не должна допускать включения в розетку только одного полюса двухполюсной вилки, а также одного или двух полюсов трехполюсной вилки.
[ПУЭ]
Для осуществления соединения при помощи розетки и вилки к розетке должен подключаться источник энергии, а к вилке - ее приемник.
[ ГОСТ 12.2.007.0-75]
Тематики
Действия
EN
DE
FR
Рис. ABB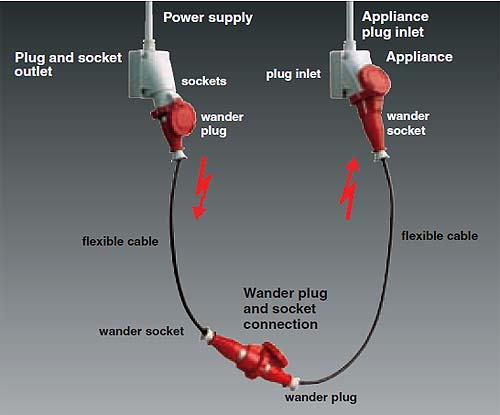
Рис. Schneider Electric
Тематики
EN
FR
кабельная вилочная (розеточная) часть электрического соединителя
Вилочная (розеточная) часть электрического соединителя для объемного монтажа, закрепляемая на конце кабеля или жгута проводов
[ ГОСТ 21962-76]
штепсель 1)
-
[IEV number 151-12-21]EN
cable connector
connector for attachment to a free end of the wire or cable
[IEV number 581-26-35]
free cable connector
connector for attachement to a free end of the wire or cable
[IEV number 581-26-09]
free connector
connector for attachement to a free end
[IEV number 581-26-10]
plug
connector attached to a cable
[IEV number 151-12-21]FR
fiche pour câble
connecteur destiné à être raccordé à l’extrémité libre d’un fil ou d’un cable
[IEV number 581-26-35]
[IEV number 581-26-09]
fiche
connecteur destiné à être raccordé à l’extrémité libre d’un cable ou d’un fil
[IEV number 581-26-10]
fiche, f
connecteur fixé à un câble
[IEV number 151-12-21]

[http://electrica-shop.com.ua/i/]
Кабельная вилка[http://electrica-shop.com.ua/i/]
Кабельная розетка1) Согласно ГОСТ 21962-76 термин штепсельный разъем является недопустимым. Поэтому применение термина штепсель представляется нецелесообразным.
К сожалению, английские и французские определения, описывающие кабельную часть соединителя, относятся как к вилке, так и к розетке. Т. е. plug может быть как кабельной вилкой, так и кабельной розеткой, что при переводе на русский язык очень неудобно.
[Интент]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
- freier Kabelsteckverbinder, m
- freier Steckverbinder, m
FR
карта технологическая
Документ, устанавливающий рациональную и стабильную технологию производства, часто повторяющегося вида строительно-монтажных работ, и используемый взамен проекта производства работ.
[РД 01.120.00-КТН-228-06]
карта технологическая
Элемент плана производства работ, определяющий технологию отдельного строительного процесса, содержащий указания по организации производства работ и труда, а также необходимые технико-экономические показатели
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- магистральный нефтепроводный транспорт
- проектирование, документация
EN
DE
FR
наконечник
Охватываемый компонент входного или выходного коннектора, предназначенный для введения в ответное гнездо специфического для медицинского газа соединения и фиксации в нем.
Примечание
В некоторых конструкциях ниппель и наконечник выполнены в виде одной и той же детали.
[ ГОСТ Р 52423-2005]Тематики
- ингаляц. анестезия, искусств. вентиляц. легких
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fiche
-
16 électrique
électrique [elεktʀik]adjective* * *elɛktʀik1) [appareil] electric; [installation] electrical; [réseau] electricity (épith)2) fig [atmosphère] electric* * *elɛktʀik adj1) (matériel, équipements, installations) electrical, (fils, câble, ligne) electric, (énergie, courant) electrical, (réseau, industrie) electricity modif (guitare, moteur, voiture, véhicule, chaise) electric2) fig (atmosphère) electric* * *électrique adj1 Tech [appareil, moteur, four] electric; [installation] electrical; [alimentation, réseau] electricity ( épith); centrale électrique power station;2 [atmosphère] electric.[elɛktrik] adjectif1. TECHNOLOGIE [moteur, radiateur, guitare] electric[système, énergie] electrical2. [par l'électricité statique] static3. [couleur] -
17 cordon-connecteur d'interconnexion
взаимосоединяющий удлинитель
-
[IEV number 442-07-06]EN
interconnection cord set
An assembly consisting of a flexible cable or cord fitted with a non-rewirable plug connector and a non-rewirable connector, intended for the interconnection of the electrical supply from one electrical appliance or equipment to another
[IEV number 442-07-06]FR
cordon-connecteur d'interconnexion
Ensemble composé d'un câble souple muni d'une fiche mobile mâle et d'une prise mobile non démontables, destiné à l'interconnexion de l'alimentation électrique d'un matériel électrique d'utilisation à un autre
[IEV number 442-07-06]EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > cordon-connecteur d'interconnexion
-
18 presse-étoupe
кабельный сальник
-
сальник для электрических кабелей и проводов
-
[ ГОСТ 4860.1-83]
[ ГОСТ 4860.2-83]EN
cable gland
device permitting the introduction of one or more electric and/or fibre optics cables into an electrical apparatus so as to maintain the relevant type of protection
[IEV number 426-04-18 ]FR
presse-étoupe
dispositif permettant l’introduction d’un ou plusieurs câbles électriques et/ou optiques dans un matériel électrique tout en maintenant le mode de protection appliqué
[IEV number 426-04-18 ]
Сальник предназначен для ввода кабелей в оболочки электротехнических изделий.
Параметры сальника:
- диаметр отверстия под сальник;
- диаметр резьбовой части сальника;
- длина резьбовой части сальника
- Сальники, устанавливаемые на корпусные конструкции... и предназначенные для уплотнения прохода одиночных электрических кабелей и проводов.
-
Уплотнение сальника должно обеспечивать:
- устойчивость к воздействию повышенного 0,3 МПа и рабочего 0,2 МПа гидростатического давления;
- непроницаемость при воздействии давления воздуха - 0,02 МПа
[ ГОСТ 4860.1-83]
Типы сальников по ГОСТ 4860. 2-83
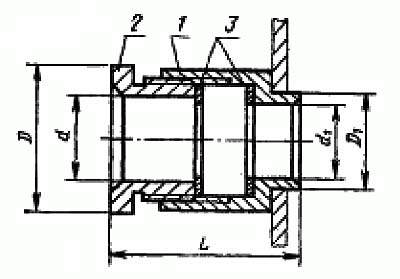
Сальник односторонний
1 - Гнездо
2 - Нажимная гайка
3 - Шайба
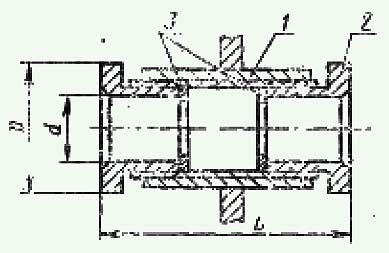
Сальник двухсторонний
1 - Гнездо
2 - Нажимная гайка
3 - Шайба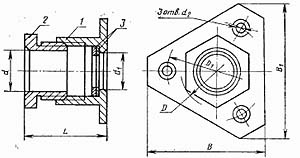
Сальник фланцевый
1 - Гнездо
2 - Нажимная гайка
3 - Шайба
Сальник трубный
1 - Гнездо
2 - Нажимная гайка
3 - Шайба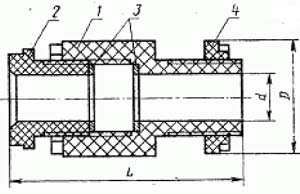
Сальник пластмассовый
1 - Гнездо
2 - Нажимная гайка
3 - Шайба
4 - Привертная гайка
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > presse-étoupe
-
19 système de goulottes
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная дляполного заключения в себяпрокладки внутри неё изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
система кабельных коробов
Система замкнутых оболочек, состоящих из корпуса со съемной или открывающейся крышкой, предназначенная для прокладки внутри нее изолированных проводов, кабелей и шнуров и/или для размещения другого электрооборудования.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61084-1 2007]
кабельнесущая система
Система закрытых оболочек, допускающая размещение изолированных проводов на базе подвижных поверхностей и предназначенная для полной защиты изолированных проводов, кабелей, шнуров, а также для размещения другого электрооборудования.
система кабельных коробов
Система закрываемых полых конструкций, состоящая из основания (корпуса) и съемной крышки, предназначенная для прокладки внутри них и защиты от механических повреждений кабелей, шнуров, изолированных проводов и (или) для размещения другого электрического оборудования, включая оборудование информационных технологий.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
Примечание. Синим цветом обозначен вариант, предлагаемый автором карточки.EN
cable trunking system
a system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electrical accessories
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
cable trunking system
system of closed enclosures comprising a base with a removable cover, intended for the complete surrounding of insulated conductors, cables, cords and/or for the accommodation of other electric equipment including information technology equipment
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
système de goulottes
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète de conducteurs isolés et de câbles, ou au logement d'autre petit appareillage électrique
Source: 826-06-04 MOD
[IEV number 442-02-34]
système de goulottes, m
ensemble d'enveloppes fermées, munies d'un fond avec un couvercle amovible et destiné à la protection complète des conducteurs isolés et des câbles et/ou au logement d'autres matériels électriques y compris des matériels de traitement de l'information
Source: 442-02-34 MOD
[IEV number 826-15-04]Обратите внимание!
Различают два вида систем кабельных коробов:
1) (просто) система кабельных коробов (cable trunking system) - система любого сечения, но обязательно с крышкой;
2) система специальных кабельных коробов (cable ducting system) - система некруглого сечения и без крышек.
Примечание. В ПУЭ короб без крышки называется глухой короб (см. кабельный короб)
[Автор карточки]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Raceways shall be one- or two-piece design with base and snap-on cover, or three-piece design with base and two snap-on covers which snap side by side on a common base.
[Legrand/Wiremold. SECTION 16130 RACEWAY AND BOXES]В состав поставки входят специальные (глухие) кабельные короба, а также кабельные короба, состоящие из основания и защелкивающейся крышки, или из основания и двух защелкивающихся крышек.
[Перевод Интент]
1 - Система кабельных коробов
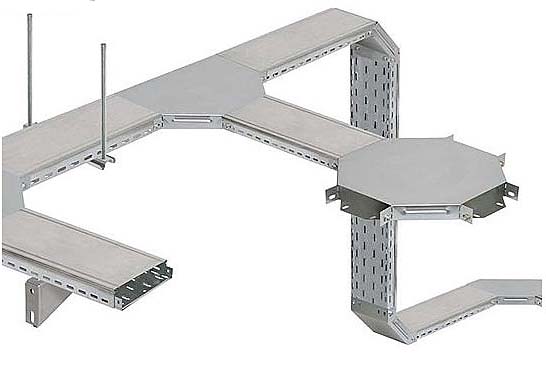
Система кабельных коробов
Система кабельных коробов
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1) - мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > système de goulottes
-
20 cordon-connecteur
шнур-соединитель
комплект, состоящий из гибкого кабеля или шнура, армированного неразборной вилкой и неразборной приборной розеткой, предназначенный для присоединения электроприбора к электрической сети
[IEV number 461-06-16]EN
cord set
assembly consisting of a flexible cable or cord fitted with a non-rewirable plug and a non-rewirable connector, intended for the connection of an electrical appliance to the electrical supply
[IEV number 461-06-16]
[IEV number 442-07-04]FR
cordon-connecteur
ensemble composé d'un câble souple, équipé d'une fiche non démontable et d'une prise mobile de connecteur non démontable destinés à relier un appareil électrique à l'alimentation électrique
[IEV number 461-06-16]
[IEV number 442-07-04]Тематики
EN
DE
- Geräteanschlussleitung, f
- Geräteanschlußleitung
- konfektionierte Leitung, f
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > cordon-connecteur
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
electrical cable — noun a cable that provides an electrical connection for telephone or television or power stations • Hypernyms: ↑cable, ↑line, ↑transmission line … Useful english dictionary
Electrical connector — Back of an audio amplifier features a variety of electrical connectors An electrical connector is an electro mechanical device for joining electrical circuits as an interface using a mechanical assembly. The connection may be temporary, as for… … Wikipedia
Cable — For other uses, see Cable (disambiguation). 6 inch (15 cm) outside diameter, oil cooled cables, traversing the Grand Coulee Dam throughout. An example of a heavy cable for power transmission … Wikipedia
Electrical wiring — in general refers to insulated conductors used to carry electricity, and associated devices. This article describes general aspects of electrical wiring as used to provide power in buildings and structures, commonly referred to as building wiring … Wikipedia
Electrical wiring (United States) — Electrical wiring in general refers to conductors used to carry electricity and their accessories. General aspects of electrical wiring as used to provide power in or to buildings and structures, commonly referred to as building wiring, are… … Wikipedia
Electrical conduit — risers, seen inside fire resistance rated shaft, as seen entering bottom of a firestop. The firestop is made of firestop mortar on top, rockwool on the bottom. Raceways are used to protect cables from damage … Wikipedia
Cable management — refers to an important step during the installation of building services (ie electrical services) and the subsequent installation of equipment providing means to tidily secure electrical, data, and other cables. The term is often used… … Wikipedia
Cable television in the Republic of Ireland — is the most common system for distributing multi channel television in the state. With a 40+ year history and extensive networks of both wired and wireless cable, the Republic of Ireland is amongst the most cabled countries in Europe.HistoryCable … Wikipedia
Electrical engineering — Electrical engineering, sometimes referred to as electrical and electronic engineering, is a field of engineering that deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable… … Wikipedia
Electrical tape — is a type of pressure sensitive tape used to insulate electrical wires and other material that conduct electricity. Itcan be made of many plastics, but vinyl is most popular; it stretches well and gives an effective and long lasting insulation.A… … Wikipedia
Electrical termination — of a signal involves providing a terminator at the end of a wire or cable to prevent an RF signal from being reflected back from the end, causing interference. The terminator is placed at the end of a transmission line or daisy chain bus (such as … Wikipedia
